Describe Common Patterns of Neuronal Organization and Processing
These paracrine mechanisms are probably crucial to normal brain. - system works in an all or none manner.
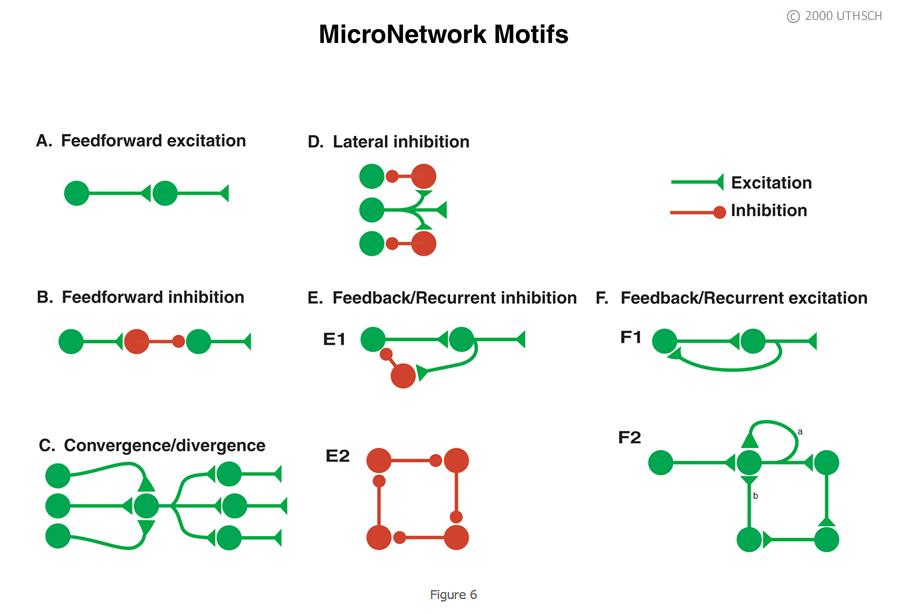
Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston
Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments.

. The mammalian retina consists of neurons of 60 distinct types each playing a specific role in processing visual images. Information arrives at a neuronal pool through one or more input neurons which branch repeatedly and synapse with numerous interneurons in the pool. Central nervous system 35.
1 central nervous system CNS-constists of the brain and spinal cord which occuppy the dorsal cavity. The formation and maintenance of this neuronal organization and interconnectivity depends on additional communication of information involving both long distance and short distance or paracrine signaling between the processes of neurons as well as with the processes of associated glial cells. High-functioning individuals occur in processing that places high demands on integration of information and coordination of multiple neural systems.
- There is the same response every time. 17 Describe common patterns of neuronal organization and processing 18 from AA 1. Describe common patterns of neuronal organization and processing.
Describe substances which are acting as chemical transmitters at a synapse or neuron junction and explain th e action of each one. Oliodendrocytes - CNS glial cells that wrap around neurons forming myelin sheaths MS is loss of this Satellite cells - PNS located function unknown Schwann Cells - PNS Forms myelin sheath in Describe five distinguishing features common to all neurons. Describe common patterns of neuronal organization and processing.
Left-Dark Right-Bright and Left-Bright Right-Dark. 2 peripheral nervous system PNS-the part of the nervous system outside the CNS consists. The dark area slightly crossed the midline in order to motivate the fish to swim toward the bright side.
The first decomposes the outputs of the rod and cone photoreceptors into 12 parallel information streams. The first decomposes the outputs of the rod and cone photoreceptors into 12 parallel information streams. The second connects these streams to specific types of retinal ganglion cells.
Neurons are different from most other cells in the body in that they are polarized and have distinct morphological regions each with specific functions. Request PDF Information Processing Neural Connectivity and Neuronal Organization Twenty years ago we proposed a neurobiological model of autism as a widespread disorder of association cortex. At this point we explore a few ways in which neuronal pools collectively process information.
Developmental Aspects of Neurons 23. Decades of research using anatomical tracing physiological recording functional perturbation and computational. It interprets sensory input and dictates motor responses based on past experience reflexes and current conditions.
Reflex to sensory to integration to motor response. Solution for Describe common patterns of neuronal organization and processing. The mammalian retina consists of neurons of 60 distinct types each playing a specific role in processing visual images.
When input is divided into many pathways in. For phototaxis two patterns were presented. We connect these properties to memory performance across recording sessions.
Start studying Objective 6. Excitability Conductivity Secretion NT Extreme Longevity Amitotic High Metabolic Rate. Start your trial now.
Describe common patterns of neuronal organization and processing. The 100 billion neurons in the brain share a number of common features Figure 1. They are arranged in three main stages.
Patterns of Neural Processing. They exhibit consistent organization in their firing pattern based on gamma phase information. - 1 neuron stimulates the next which stimulates the next in a simple chain of neurons.
A cooperative associative input-specific and anti. Threshold resting membrane potential polarized state depolarized state repolarization refractory period 5. First week only 499.
The hippocampal formation is. We will now describe the typical patterns for the hippocampus neocortex and the entorhinal cortex in some more detail. Relate growth to mitosis and significance of synapses.
Although individual neurons can themselves be sophisticated information-processing units it is their synaptic connection patterns that enable neurons to form specialized circuits for specific functions making the brain a powerful computational device. Dendrites are the region where one neuron receives connections from other neurons. Some input neurons form multiple synapses with a single post-synaptic cell.
The visual stimulation consisted of serial repetitions of different sets of patterns. Indeed different forms of synaptic plasticity could be directly involved in generating specific brain networks characteristics. Describe or identify the following properties of a synapse.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. As the book title indicates the focus is on tumours of the central nervous system includ-ing tumours of cranial and paraspinal nerves. Finally we describe how human neuronal assemblies flexibly adjust6-9.
The hippocampus forms a three-layered allocortex in the depth of the temporal lobe. After each pattern a period of whole field dark was presented. Synaptic plasticity mechanisms and specific features of brain network share common principles that contribute to explain how neural plasticity influences brain network organization.
The second connects these streams to specific types of retinal ganglion cells. They can produce EPSPs at all points of. It receives strong input from the entorhinal cortex to which it also projects thereby forming a synaptic loop.
Distinguish between serial and parallel processing. Describe and identify the following characteristics of neurons. Describe how neurons originate and mature.
They are arranged in three main stages. Divided into 2 different division.

How Do Sensory Neurons Sense Danger Signals Trends In Neurosciences

Neuronal Pools And Neural Processing Youtube
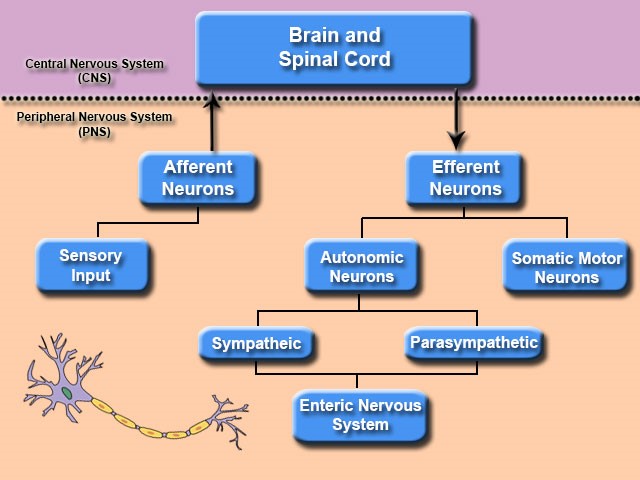
Organization Of The Nervous System

Pdf Natural World Physical Brain Operational And Mind Phenomenal Space Time
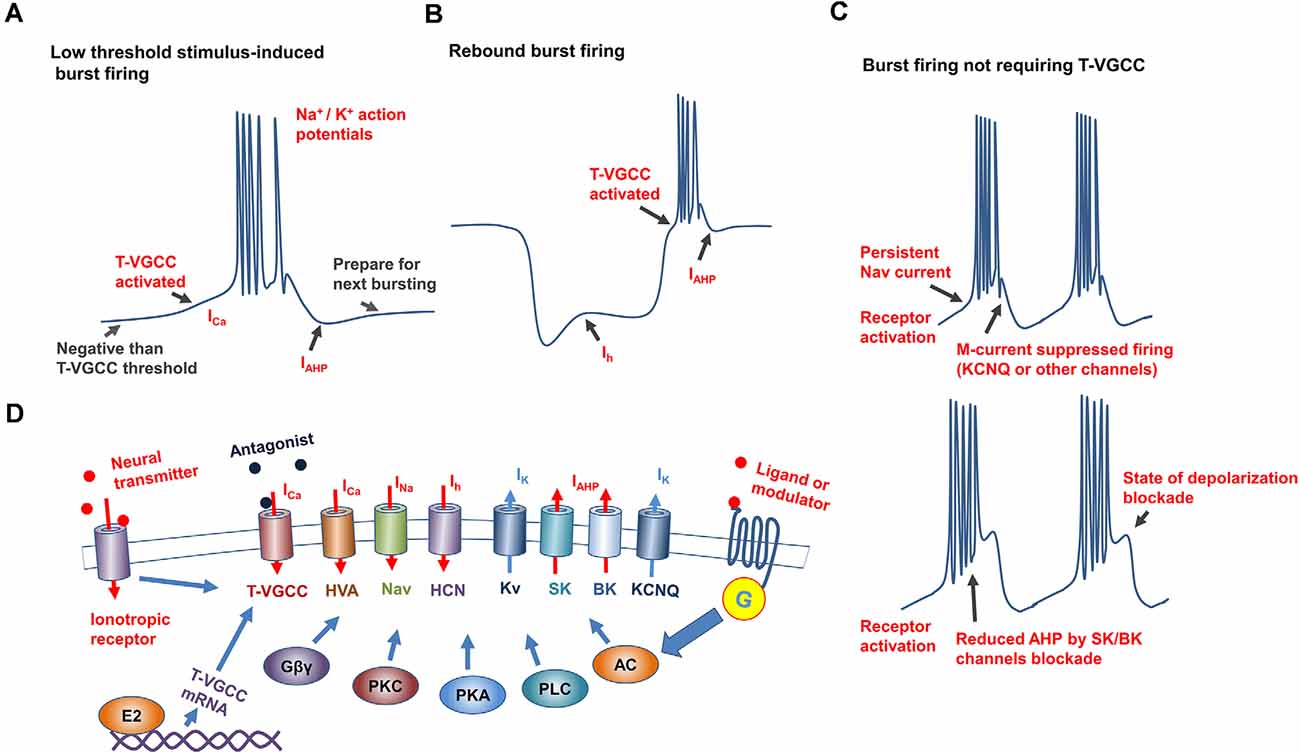
Frontiers Neural Burst Firing And Its Roles In Mental And Neurological Disorders Cellular Neuroscience
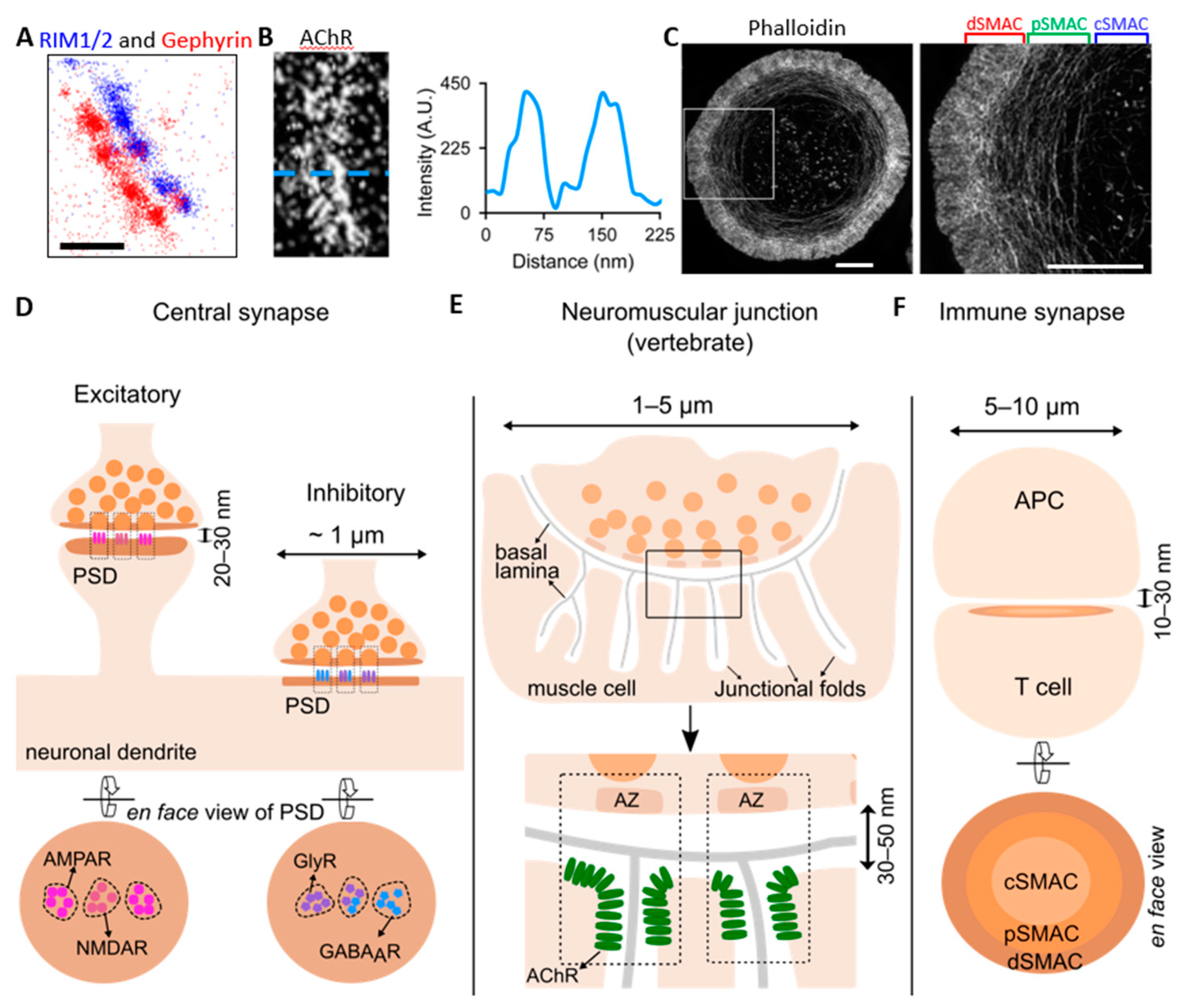
Membranes Free Full Text The Nanoscopic Organization Of Synapse Structures A Common Basis For Cell Communication Html

Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston
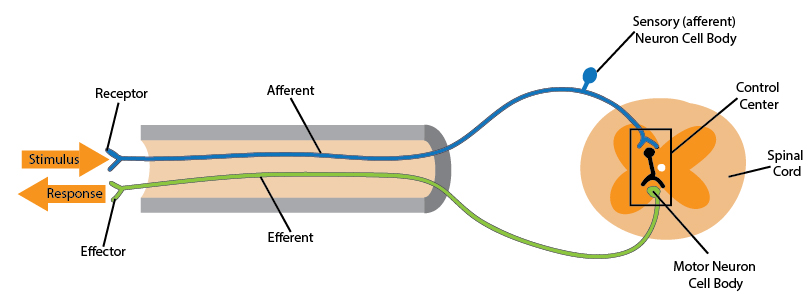
Organization Of The Nervous System
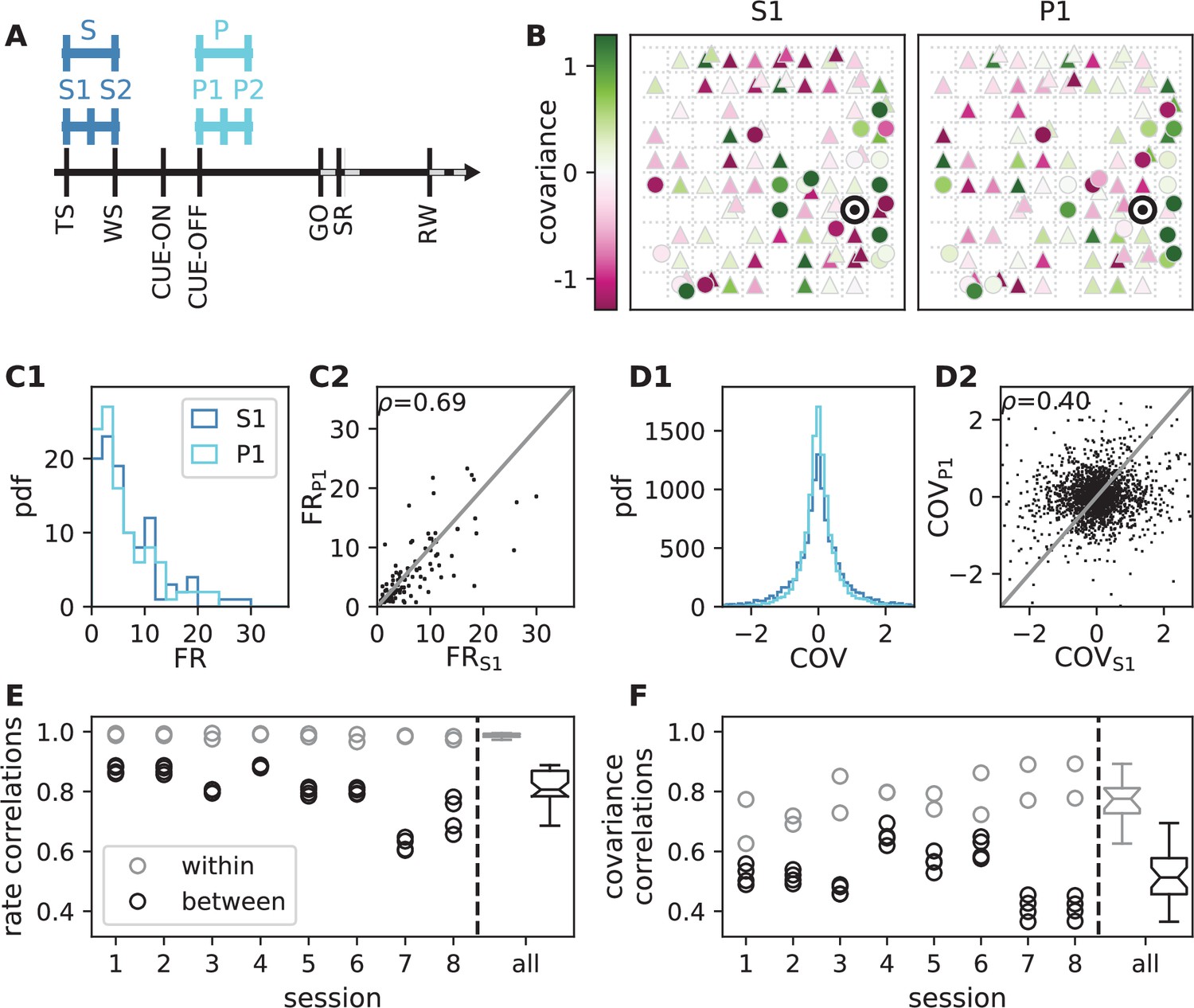
Global Organization Of Neuronal Activity Only Requires Unstructured Local Connectivity Elife
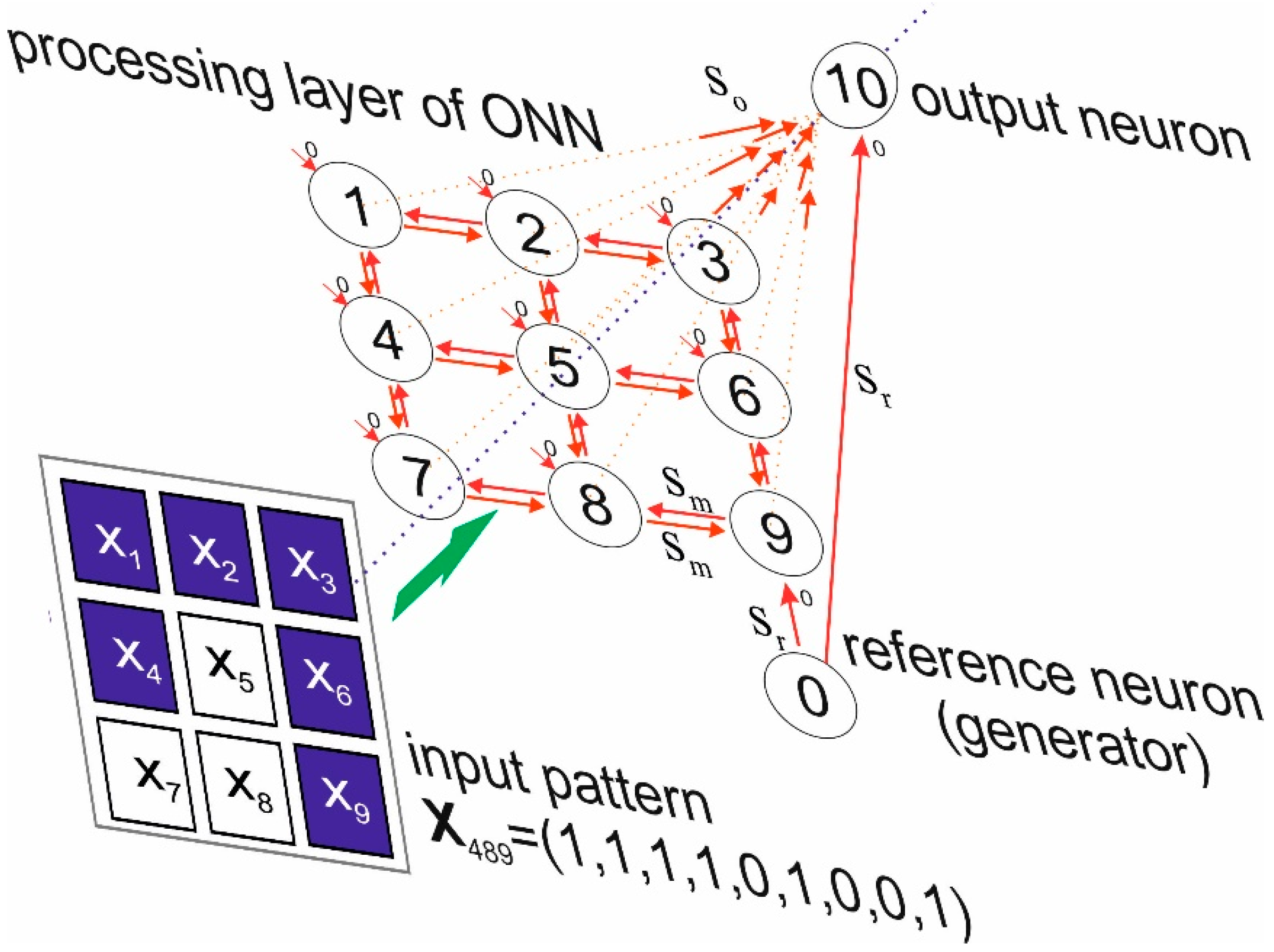
Electronics Free Full Text A Model Of An Oscillatory Neural Network With Multilevel Neurons For Pattern Recognition And Computing Html
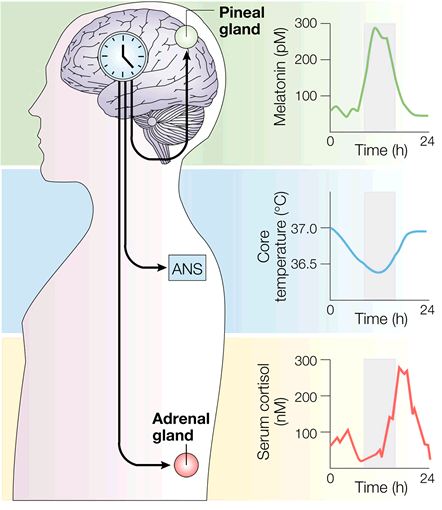
Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston
4 1 The Neuron Is The Building Block Of The Nervous System Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition

Artificial Neural Network An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Frontiers Circuit Organization Underlying Optic Flow Processing In Zebrafish Frontiers In Neural Circuits

Neuronal Pools And Neural Processing Youtube

Neuronal Pools And Neural Processing Youtube
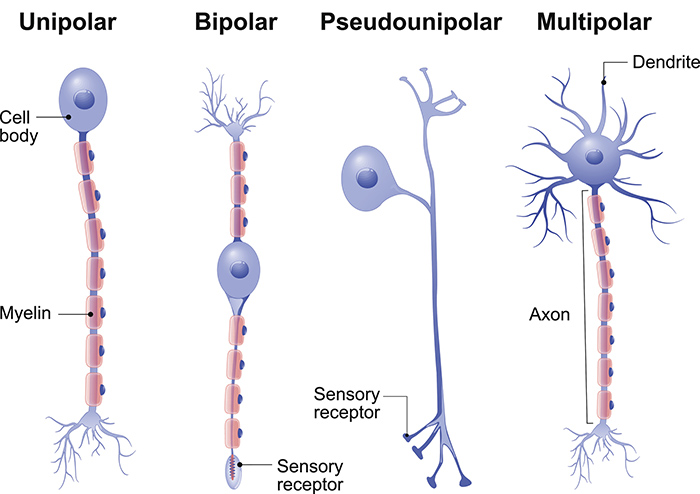
Types Of Neurons Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland


Comments
Post a Comment